Treatment Areas
Treatment Areas
- +
- +
- MAIN PAGE +
- BIOGRAPHY +
- +
- GALLERY +
- CONTACT +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- +
- Prof. Dr. +
- Treatment Areas +
- - Multiple Sclerosis
- - Epilepsy - Sara's Disease
- - Alzheimers
- - Dementia
- - Dementia, Alzheimers
- - Migraines and Headaches
- - Parkinson's Disease
- - Sleeping disorders
- - Stroke - Paralysis
- - Hand, Foot Numbness
- - Muscle Weaknesses
- - Peripheral Neuropathy
- - Brain Related Infections - Tumors - Degenerative Diseases
- - EMG - Electromyography
- - EEG Recording - Electroencephalogram
- - Long Term Video EEG
- - Visual Evoked Potentials - VEP Test
- +
- - Diagnosis and Treatment
- - What is Multiple Sclerosis?
- - Alzheimer's Disease
- - Epilepsy
- - How Should
- +
- +
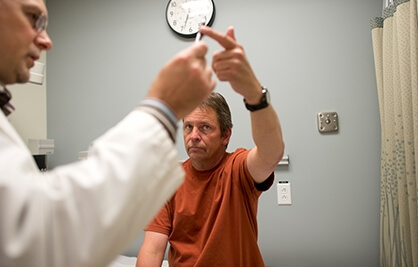
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis (MS), a chronic disease of the central nervous system, is estimated to affect more than 2.3 million people worldwide.
More
Epilepsy - Sara's Disease
Epilepsy is a neurological problem that causes strange sensations, convulsions, and loss of consciousness as a result of disruption of neuronal activity in the brain, and various other seizure-related symptoms.
More
Alzheimers
Alzheimers disease is a progressive neurological disorder that causes the brain to shrink (atrophy) and die of brain cells.
More
Dementia
Dementia (dementia) is the general name for symptoms that affect memory, thinking and social skills so severely that they interfere with daily life. Dementia is not a disease name. More than one disease can cause dementia.
More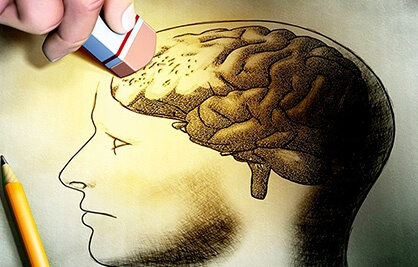
Dementia, Alzheimers
Alzheimers Disease is the most common cause of dementia and is an irreversible progressive disease.
More
Migraines and Headaches
Headache is one of the most common complaints in society. A comprehensive neurological examination is required for the appropriate approach in headaches that occur for many different reasons.
More
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative, progressive brain disease that causes symptoms as a result of the gradual loss of function of nerve cells called neurons in the brain.
More
Sleeping disorders
Sleep is critical to both your daily life and your physical and mental health. Problems falling asleep or staying asleep, respiratory distress during sleep, and excessive daytime sleepiness are among these disorders.
More
Stroke - Paralysis
A stroke is a medical emergency that occurs when the blood supply to part of your brain is interrupted or significantly reduced.
More
Hand, Foot Numbness
Numbness or tingling, which is generally defined as a pricking, burning, stinging sensation, often occurs in the extremities, but may be a common finding of many different neurological diseases.
More
Muscle Weaknesses
Muscle weakness can occur anywhere in the body. This problem can be in a single muscle or it can affect certain muscle groups. In some cases, widespread muscle weakness can be observed. The first step to effectively managing the weakness is why
More
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral Neuropathy causes weakness, numbness, and pain, usually in your hands and feet, as a result of damage to your peripheral nerves.
More
Brain Related Infections - Tumors - Degenerative Diseases
Brain diseases occur in different forms. Infections, trauma, stroke, seizures, and tumors are some of the main categories of brain diseases.
More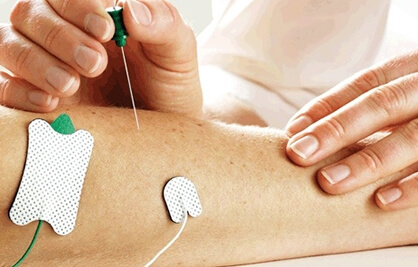
EMG - Electromyography
An EMG is a diagnostic test that evaluates the health of your muscles and the nerves that control them. It measures muscle response or electrical activity in response to nerve stimulation.
More
EEG Recording - Electroencephalogram
An EEG (Electroencephalogram) is a neurological test that measures the electrical activity of your brain.
More
Long Term Video EEG
Long-term video EEG monitoring; It is a method in which EEG recording can be made uninterruptedly for hours and days in a way that the patient's behavior can be seen in detail and clearly accompanied by video.
More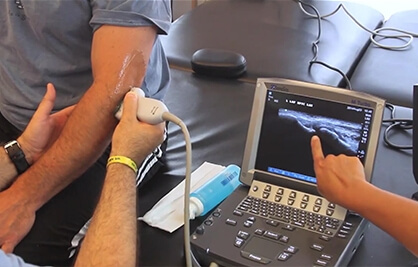
Visual Evoked Potentials - VEP Test
As your body experiences light, sound, touch, and other sensations, your brain receives this information as a series of electrical signals.
More